
Pelvic Anatomy Xray Female pelvis bones and joints, Xray Stock Image C033 It first
The pelvis series examines the main pelvic ring, obturator foramina, sacroiliac joints, symphysis pubis, acetabulum, sacral foramina, and the proximal femur. The AP pelvis has a diagnostic yield of ~94% in severely injured patients 2,3. See an approach to the pelvic radiograph. Indications

👨🏽💻Want to learn a system for reviewing a pelvic Xray? Read on to find out and swipe left to
Each hemi-pelvis bone comprises 3 bones - the ilium ( white ), pubis ( orange) and ischium ( blue) The 3 bones fuse to form the acetabulum - the pelvic portion of the hip joint. ASIS = Anterior Superior Iliac Spine = attachment site for sartorius muscle. AIIS = Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine = attachment site for rectus femoris muscle.

Pelvic X Ray Lines Pelvis AP Xray of 66yearold female. White arrow / Shenton's line is
What are the techniques for pelvic x-ray and CT? 5. How should x-ray and CT of the pelvis be interpreted? 6. Who needs pelvic x-ray following trauma? 7. When pelvic x-ray is normal, who needs CT? 8. If CT is planned for evaluation of other abdominal and pelvic soft-tissue injuries, is x-ray needed? If so, in which patients? 9.

normalmalepelvisannotated
Figure 1: three rings. Case 1 (a): subcaptial fractured neck of femur. Figure 2: joint spaces. Case 1 (b): intertrochanteric fracture. Figure 3: acetabulum. Case 2: pubic ramus fracture. Figure 4: acetabular radiological anatomy. Case 3: complex open book fracture. Case 4: acetabular fracture.
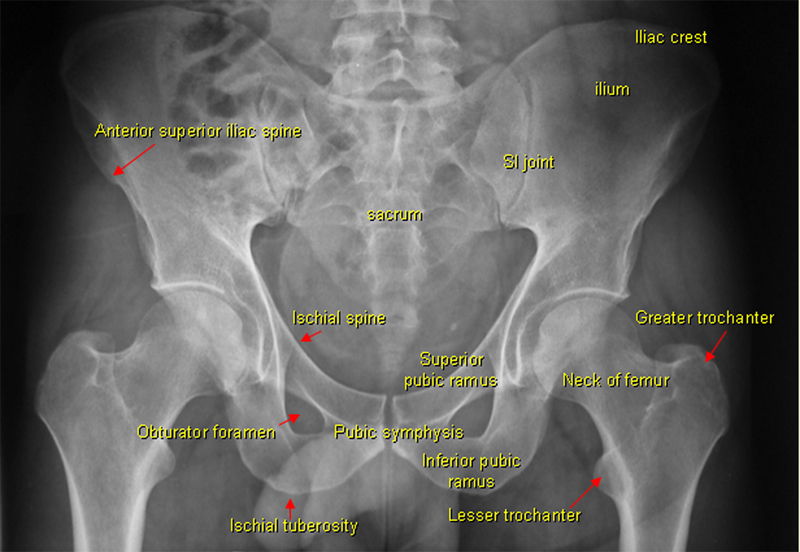
Pelvic Anatomy Xray Interpreting X Rays Of The Pelvis Hip Joint And Femur Youtube Each hemi
Anatomy of the Pelvis. The pelvis is a ring of bones situated between the spine and the legs. The pelvis is composed of three bones (2):. The sacrum, a triangular bone at the bottom of the spinal column; The coccyx, also referred to as the tailbone; The hip bones, also known as the pelvic girdle, comprise three fused bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis; X-ray Views of the Pelvis

Female pelvis bones and joints, Xray Stock Image C033/7354 Science Photo Library
A pelvis x-ray will allow a radiographer or doctor to spot different ailments. For example, if there's a break in the bone then light will seep through in the x-ray and highlight where the injury is. X-rays are also able to show abnormal matter, which may represent a tumour.
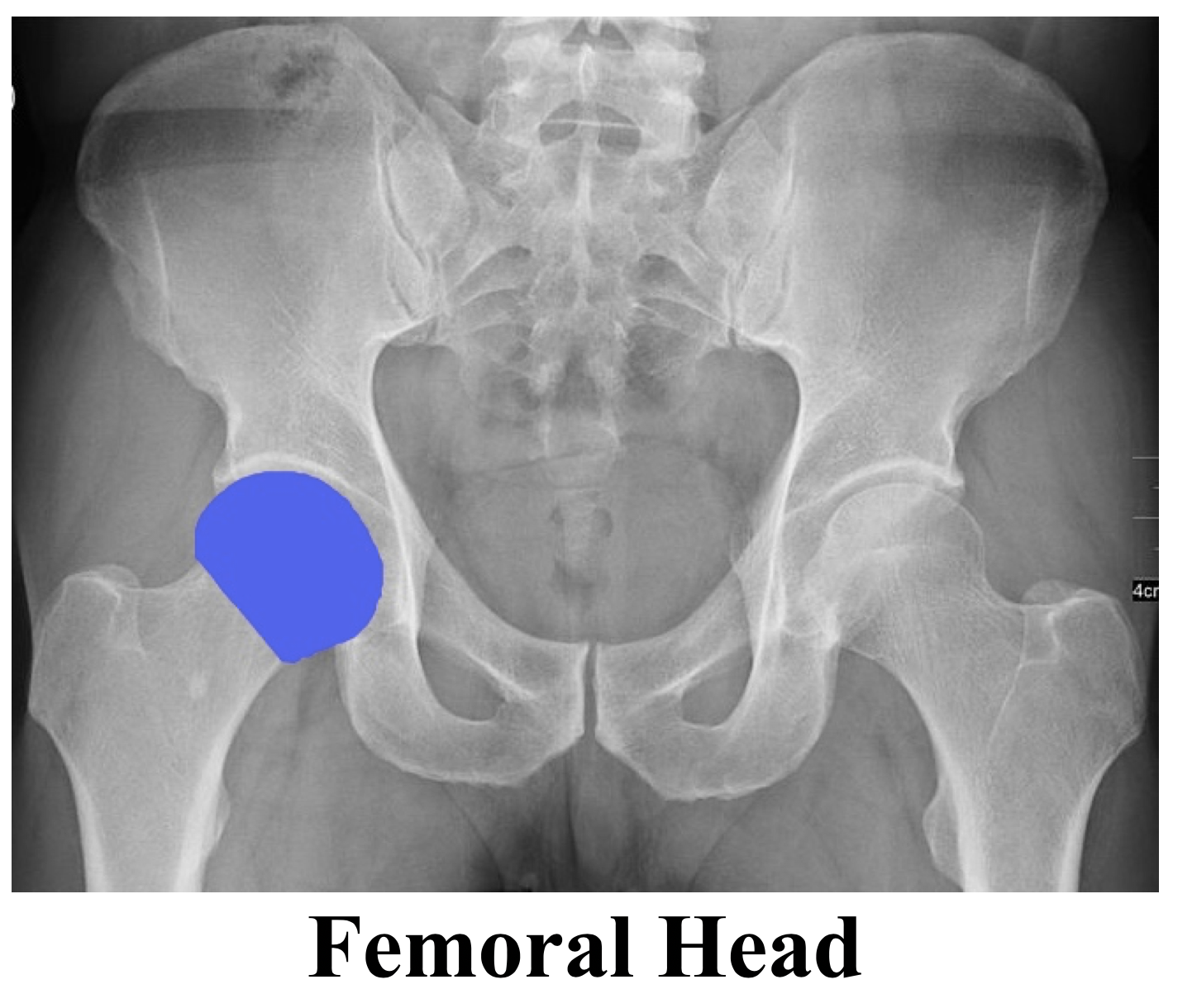
Back to Basics Pelvic XRays — Taming the SRU
The term pelvis (plural: pelvises or pelves) can refer to either the bony pelvis or the pelvic cavity. Bony pelvis The bony pelvis is formed by the sacrum and coccyx and a pair of hip bones ("ossa coxae"), which are part of the appendicular skeleton.
Pelvic Anatomy Mri Human Anatomy
For the purpose of this article, we will concentrate on a systematic approach to interpreting hip X-rays with an antero-posterior (AP) view, which is the commonest and most likely to be presented to you in an exam situation. Confirm details Begin by confirming you have the correct patient and the correct radiograph by assessing the following:
Pelvic Anatomy Xray Tomas Ho
Diagnosing tumours. Preparation There is no preparation required for a pelvis x-ray. It is important to inform a member of staff as soon as possible if you are pregnant or suspect you are pregnant BEFORE the test is performed. The examination may not be appropriate or special considerations or precautions might need to be taken. Procedure

Pelvis xray Stock Image C019/7257 Science Photo Library
A pelvic X-ray is a type of X-ray that captures detailed images of the pelvic region, which includes the pelvis, hips, and upper legs. Healthcare professionals use these X-ray studies (radiographs.

pelvis radiographic anatomy Normal vs OA Medical radiography, Medical ultrasound, Medical anatomy
This article lists a series of labeled imaging anatomy cases by body region and modality. Brain CT head: non-contrast axial CT head: non-contrast coronal CT head: non-contrast sagittal CT head: non-contrast axial with clinical questions CT head: angiogram axial CT head: angiogram coronal CT head: angiogram sagittal CT head: venogram axial

Pelvic Anatomy Xray Pelvic Xray Stock Image P116/0713 Science Photo Library
Description Labeled AP Pelvis XRay Anatomy - Female #Anatomy #Radiology #Pelvis #XRay #Labeled #Female Contributed by Dr. Gerald Diaz @ GeraldMD Board Certified Internal Medicine Hospitalist, GrepMed Editor in Chief 🇵🇭 🇺🇸 - Sign up for an account to like, bookmark and upload images to contribute to our community platform.

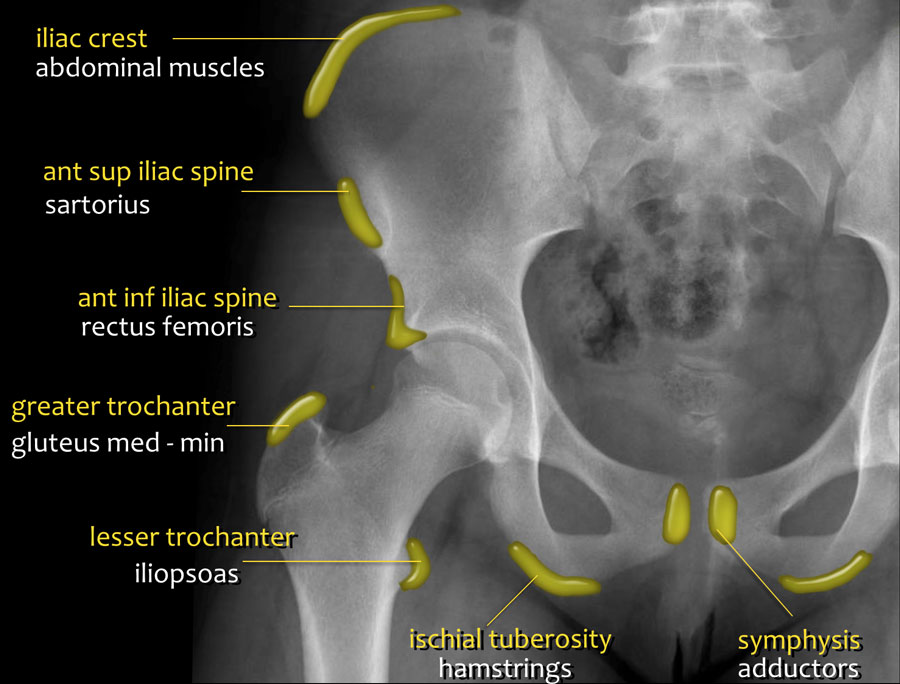
Take a look at this annotated XRay, which exhibits you the place a number of the pelvic musc
35 cm x 43 cm exposure 70-80 kVp 20-30 mAs SID 100 cm 2 or 120 cm 3 grid yes Image technical evaluation entirety of the bony pelvis is imaged from superior of the iliac crest to the proximal shaft of the femur 2 obturator foramina and acetabular teardrops appear symmetrical and midsacral line aligns with the pubic symphysis 2,3

Pelvic Bone Anatomy Xray Mamie Stewart
Introduction. This e-Anatomy module is dedicated to the radiological anatomy of the thorax (chest, mediastinum, lungs, pleura, mediastinal vessels) and abdomen-pelvis (digestive system, kidneys). It has been designed to help radiologists in their daily practice as the chest x-ray is the most frequently prescribed radiological examination.

44+ Pelvis X Ray Anatomy Pics
1. Hand The following is a normal, labelled, hand x-ray: Labelled Hand Labelled Hand ODIN Link to Labelled Images - https://mistr.usask.ca/odin/?caseID=20110802102214107 2. Wrist The following is a normal, labelled, wrist x-ray: Labelled Wrist Labelled Wrist ODIN Link to Labelled Images - https://mistr.usask.ca/odin/?caseID=20110802102041021 3.

Pelvic Anatomy Labeled Pelvis Wikipedia
During the secondary survey, pelvic bones are not stable, and there is a pain on palpation. You placed a pelvic binder and ordered a pelvic X-ray. Important Anatomical Considerations. The three bones compose the pelvis (the sacrum and the two innominate bones). Strong ligaments keep these three bones together.